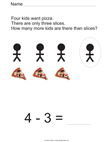Mathematics - Common Core Standards
Operations and Algebraic Thinking for Grade 1
Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction.
|
|
|
 |
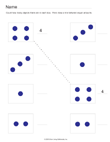
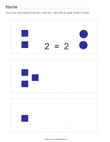
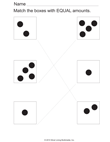
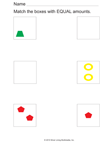
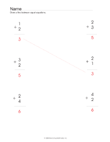
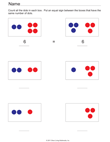
Quick Assessment for 1.OA.1 and 1.OA.2 |
- 1.OA.1. Use addition and subtraction
within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of adding
to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing,
with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using objects,
drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to
represent the problem.1
Addition Word Problems
Subtraction Word Problems
- 1.OA.2. Solve word problems that call
for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is less than or
equal to 20, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations
with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.
Understand and apply properties of operations and the
relationship between addition and subtraction.
- 1.OA.3. Apply properties of operations
as strategies to add and subtract.2 Examples: If 8
+ 3 = 11 is known, then 3 + 8 = 11 is also known. (Commutative
property of addition.) To add 2 + 6 + 4, the second two numbers
can be added to make a ten, so 2 + 6 + 4 = 2 + 10 = 12.
(Associative property of addition.)
- 1.OA.4.Understand subtraction as an
unknown-addend problem. For example, subtract 10 – 8 by
finding the number that makes 10 when added to 8. Add and
subtract within 20.
Add and subtract within 20.
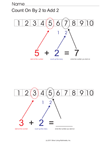
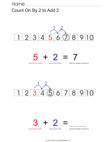
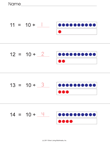
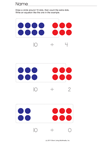
- 1.OA.5. Relate counting to addition and
subtraction (e.g., by counting on 2 to add 2).
- 1.OA.6. Add and subtract within 20,
demonstrating fluency for addition and subtraction within 10.
Use strategies such as counting on; making ten (e.g., 8 + 6 = 8
+ 2 + 4 = 10 + 4 = 14); decomposing a number leading to a ten
(e.g., 13 – 4 = 13 – 3 – 1 = 10 – 1 = 9); using the relationship
between addition and subtraction (e.g., knowing that 8 + 4 = 12,
one knows 12 – 8 = 4); and creating equivalent but easier or
known sums (e.g., adding 6 + 7 by creating the known equivalent
6 + 6 + 1 = 12 + 1 = 13).
Work with addition and subtraction equations.
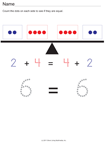
- 1.OA.7. Understand the meaning of the
equal sign, and determine if equations involving addition and
subtraction are true or false. For example, which of the
following equations are true and which are false? 6 = 6, 7 = 8 –
1, 5 + 2 = 2 + 5, 4 + 1 = 5 + 2.
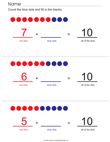
- 1.OA.8. Determine the unknown whole
number in an addition or subtraction equation relating three
whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that
makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 + ? = 11, 5 =
_ – 3, 6 + 6 = _.
The Common Core State Standards are ©
Copyright 2010. National Governors Association Center for Best
Practices and Council of Chief State School Officers. All rights
reserved. For more information about the Common Core State
Standards, visit their website at
http://www.corestandards.org
Click on any of the standards on the left to create custom
worksheets or to print premade materials.
The Common Core State Standards are ©
Copyright 2010. National Governors Association Center for Best
Practices and Council of Chief State School Officers. All rights
reserved. For more information about the Common Core State
Standards, visit their website at
http://www.corestandards.org
 Adaptive Worksheets
Adaptive Worksheets